RFID Info
RFID Functionality
We are incredibly excited to announce that RFID functionality has finally arrived in Flex! It has been talked about and debated for years now, and we feel that the hardware and the software have come to the point that we are confident in the accuracy and usability of RFID inside rental and production warehouses. With the release of Flex5 v26, now available on for both Tablet and Phones, on both Android and Apple devices, RFID functionality is available as a new add on module for our customers. As of now, RFID is available as a free preview functionality to select customers for testing purposes, however, in the future, this functionality will be an additional cost per billing cycle, whether you had preview access to the RFID functionality or not. To inquire about early access testing of RFID with your existing service, please contact support@flexrentalsolutions.com.
RFID Background
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology was developed in the 1940s and has been in commercial use for more than 30 years. RFID technology has been implemented by companies large and small to identify and keep track of their assets and inventory. RFID is commonly used in applications as varied as railway-car tracking, toll-road control, farm-animal identification, and retail theft control. Rental Management, especially that with a complex warehousing workflow and processes such as those used in the live event industry, has historically struggled with successful RFID implementation. Our goal has been to take the "best-of-breed" warehousing processes found in Flex; add near-field batch capturing of RFID asset tags to make the capture much more efficient, while still maintaining the balance of accuracy.
Time and cost savings are the primary advantages of replacing Barcode Tracking with RFID. A comprehensive study by Shayne Pidding for RAMP RFID states an organization with about 100,000 assets can save up to $150,000 with implantation of RFID-based asset tracking technology. Our early estimates are that our customer who implements RFID technology will see a 6x - 10x speed improvement of asset ID capturing, which could greatly improve efficiency in the warehouse process. When potential implementers see possible savings such as these, there is a tendency to think that all work and accountability are a thing of the past and now technology will do all the work for them, far from it. Adding RFID on top of poor warehousing software just gets the user to an inferior end product faster. Similarly, adding RFID to an undisciplined and a loosely defined warehouse process gives you only marginal advantages. Ideal candidates for RFID have an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of RFID, and that is not a magic pill that solves all problems. It should improve the speed at which you capture the identification of the items you are tracking, however, because RFID is not a line of sight capture such as barcode scanning, the possibilities are present that the user might capture tags nearby unexpectedly depending on different setups. Setting realistic expectations and understanding advantages and disadvantages of different workflows, warehouse setup and Tag types will greatly effect the final outcome.
"Begin with the End in Mind"
Steven R. Covey had great insights into productivity. The concept of "Beginning with the end in mind" is constructive to discuss how you might implement RFID in your warehouse process. If the end manifest is a linear list of gear, then storage or free pick containers are not necessary. RFID tags can be added on shipping cases, and they can be captured as part of the capture of RFID Tags with the rest of the inventory. The process of capturing all tags in a straight list of items is a more straightforward process where you are prepping all gear during the prep process.
However, if you are looking for a manifest of gear that details what inventory is contained inside each shipping case, with the ability to print show or shipping case labels with a list of shipping case contents, then that will dictate a different warehouse workflow process to get to your goal. The RFID capture process cannot know what items are inside each case if cases and assets all have RFID Tags and you simply sweep all RFID Tags with the reader during the prep process. If the goal is to build what assets are inside which shipping case, then the users would use a few different inventory types to build case contents in the warehouse process. We would recommend keeping BarCodes on the shipping cases and adding RFID to all other assets.
Storage Container functionality allows users to prepare the shipping cases to be “show ready,” before putting the shipping case on the shelf through the Container Building process. During the prep process, the user scans out the shipping case with the pre contained items directly to the manifest. This makes the prep process extremely fast as then you simply scan the barcoded cases during the prep process which adds the case with its pre prepped contents to the manifest with one scan. After returning all items during the return process, the user would then rebuild the case before putting them on the shelf by scanning the barcode for the shipping case in container builder, then RFID sweep the contents to fill the shipping case with the required contents. Finally, scan the shipping case barcode to close the case. Repeat as necessary for other cases.
Serialized Packages are similar to Storage Containers, in that they are prebuilt prior to the prep of a job. However the return process is different. Serialized Packages get built once and prepped. On the return the contents get auto returned and their contents stay intact, where Storage Containers require a return of the shipping case and contents. The Contents are removed during the return process to rebuild the shipping case contents with what ever items are in the shipping case during the return.
The second feature for building shipping case contents is called Free Pick Containers. These are typically empty shipping cases that get filled during the prep process of a show. During the prep process, before scanning or RFID capturing the tags, just scan the barcode of the Free Pick Container shipping case to virtually open the case, then RFID capture the items as you add them to the contents of the shipping case, and finally scan the barcode of the Free Pick Container shipping case to virtually close the case.
Whether using Storage Containers, Free Pick Containers or Serialized Packages, the end manifest is ready for case labels and reports of case value and weight per case.
Value-Manifest-Custom.xls - Compatibility Mode.pdf
Frequency Ranges
Low Frequency: >134kHz
- A globally-used frequency for applications such as access control, animal id and service industries.
- This frequency has the least problems with metal and liquids.
High Frequency: 13.56 MHz – nowadays also more known as NFC standard as you can also communicate on this standard with certain smartphones and tablets.
- A globally-used frequency for applications includes tracking library books, patient flow tracking, and transit tickets.
- HF RFID systems work in ranges of inches, but they can have a maximum read range of about three feet (1 meter).
Ultra High Frequency: 868MHz Europe / 915 MHz USA / 950 MHz Japan / 918-926 MHz Australia
There are standards existing on the communication, but the frequency is still regionally determined.
- UHF frequencies typically offer much better read range (inches to 50+ ft. depending on the RFID system setup) and can transfer data faster (i.e. read many more tags per second) than low- and high-frequencies.
- However, because UHF radio waves have a shorter wavelength, their signal is more likely to be attenuated (or weakened) and they cannot pass through metal or water.
- Due to their high data transfer rate, UHF RFID tags are well-suited for many items at once, such as boxes of goods as they pass through a dock door into a warehouse or racers as they cross a finish line.
- Also, due to the longer read range, other common UHF RFID applications include electronic toll collection and parking access control.
- Based on these characteristics, UHF frequency tags are best suited for high volume inventory tracking of assets.
- Some Tags are Global-UHF capable, meaning that the antenna can receive radio frequency over a broader range and can be read by both USA and European readers. Multi-national companies should consider this if inventory will be transferred between
FLEX ONLY RECOMMENDS UHF FOR USE WITH OUR APPLICATION
RFID Readers
There are many different types of scanners available. We have implemented the RFID acquisition process into our HTML5 web-based app for both Tablets and Phones. In the future, we will also support connecting similar devices in the replacement Flex5 Desktop environment also. To simplify the connection of these devices in all environments, we have chosen to connect to devices that support Bluetooth connections. Many devices support both SDK and HID based connection modes. For simplicity sake, we have chosen HID mode as this will support the same device, once configured correctly, to work in both apps and desktop browsers. Because we are using HID Mode, the app believes there is a keyboard attached. The device acts similar to a keyboard, and after acquiring the ID from the backscatter, it sends the data via Bluetooth as if a keyboard typed it in. One thing to realize with Apple devices is when you click in a field that the device expects the user to enter text, the keyboard automatically appears. Most devices allow some form of a shortcut to auto-hide the keyboard because the data will be streamed directly from the device instead of typing it in. The Device we have standardized on at present is the Zebra RFD8500 which allows Bluetooth connection in HID Mode. It also will enable the user to auto-hide the onscreen pop-up keyboard with a double pull of the device trigger (make sure not to have the device near any tags during this process, or sometimes a reader can falsely send tags data into the app text field.
FLEX ONLY RECOMMENDS THE ZEBRA RFD8500 RFID/1D/2D SLED
The RFD8500 will automatically remove any duplicate tag ID's received during a more extended RFID capture period if the trigger is held down, and not transmit those duplicates to the app. The automatic duplicate tag removal will improve the speed of the reception of all tag data.
This unit comes in different global regions (i.e US or EU) and with or without barcode scanner, we recommend the version with a barcode scanner, make sure to purchase the correct version.
To get the Reader Flex ready, you will need a windows computer or a windows emulator running on an Apple desktop or laptop such as Parallels.
You will need to download Zebra's 123Scan Utility. You can update the firmware if you wish. (R55 Tested and Working).
To update the Zebra RFD8500 with the new plugin, Download Here. Under Tools, Import this Plugin.
Load this existing config file and "load to scanner" to turn the scanner into Bluetooth HID Mode, allow double trigger pull to enable the user to toggle the onscreen keyboard on and off.
Barcodes Inc is a great supplier for these devices.
RFID TAGS
There are two types of Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags that can be affixed to physical assets - “passive” and “active.”
Active tags require a battery that continuously broadcasts a signal with longer read ranges while passive tags do not need an internal power source and powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. Passive tags remain silent until energized by a scanner which then reads the unique code, reducing extraneous signals.
Passive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead receive their power by converting the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. It is common practice to use Passive RFID tags in high volume asset tracking environments as the lower price point per tag makes employing passive RFID systems economical.
Passive RFID tags only have two main components – the tag’s antenna and the microchip or integrated circuit (IC).
As the name implies, passive tags wait for a signal from an RFID reader. The reader emits energy out on a specified frequency band. The internal antenna in the RFID tag draws in energy from the RF waves and sends that energy into the read zone of the IC Chip. With enough power, the chip generates a signal back to the RF system. The data transmitted back from the IC chip is called backscatter. The Reader receives this backscatter from the tag via the antenna and sends that data to the application.
Passive / Active Tag Similarities
- Both use electromagnetic energy.
- Line-of-sight is not required for either to acquire RFID data of assets.
- Both enable readers to detect and identify objects.
Passive / Active Tag Differences
- Passive tags have a read range of 20 feet with handheld readers, while active tags can have a read range as broad as 750 feet. It should be noted, however, that longer read ranges can create an issue with signal interference and the unintended reading of other tagged assets in the area.
- Passive tags have an unlimited lifespan while the battery-powered active tags last between 1 - 3 years.
- Passive tags are less expensive, generally ranging between $0.16 and $2.50 apiece while active tags can run between $30 - $80.
- Passive Tag sizes come in a broader range of sizes. Some are as small as a large grain of rice while others are as large as a small candy bar. Typical active tags range from the size of a small candy bar and larger.
Countless types of passive RFID tags exist on the market, but all tags generally fall into two categories – inlays or hard tags. Thin labels or stickers are typical examples of RFID Inlays. Hard RFID tags are more durable and made of plastic, metal, ceramic and even rubber. They come in all shapes and sizes and for unique functions, materials, and applications.
FLEX ONLY RECOMMENDS THE PASSIVE TAGS
TAG EXAMPLE
*This is a real work in progress and will be updating as we get more feedback from real users. *
PrePrinted Tags with BarCode and RFID
The Universal Series of RFID / Barcode Labels are the closest thing to a "one-size-fits-all" RFID solution we have found. Tags work well on both Metal and Non-Metal Assets. The ability to have both a barcode printed on the label and the RFID tag inlay makes an ideal tag from a vast amount of inventory. These come in three different sizes. Typical read distance is about 2'. Typically these stickers can have both a barcode, as a backup for the RFID tag and the RFID Inlay.
Contact Info
Laura Marzen
855-747-3594
Usage possibilities
Cases
Truss
LED Tiles
Speakers
Rack Gear
Laptops
Stage Decks
Vizinex are makers of aftermarket cable clamps/housing are a great way to add RFID to existing cable supplies. The shells clamp around different sizes of cable from standard 12/3 power cables all the way up to 6 cable breakout bundles. The housings have an area to captivate a tie line. In the future, they have plans to release smaller housings for cables with smaller diameters.
On Metal Tags
Xerafy makes some great on metal tags.
Hubble Wiring Devices
Makers of many great electronic connectors.
Please contact support@flexrentalsolutions.com to help with recommendations. In the future, Flex will offer an online retail store to purchase devices and tags to help our customers.
WAREHOUSE ENVIRONMENT
There are a few aspects to consider in the implementation of RFID in the warehouse process. Reader/Receiver Sensitivity, Tag Type/Tag Strength and warehouse environment and the available space will significantly affect the implementation and how overall successful it will be.
The sensitivity at which the reader receives information back from the is important in warehousing environments. Too high and you are getting more unexpected assets in your capture. Too small and the reader needs to be in very close proximity to the tag to read the ID.
In the real world, if you are scanning items, a barcode reader would only scan the barcode within the capture area of the scanner. However, the RFID reader receives all ID's within proximity of the read field. If the combined read strength of the tags and the reader are high, then you might capture more unexpected ID's.
Barcodes can be scanned within proximity to other barcoded assets without any real concern for unexpected scans. Tag type and size will significantly affect read distance. More extended read distance tag types have advantages and disadvantages. It is very common for gear to be stored side by side, and on shelves above and below similar and dissimilar inventory. Often warehouse aisles have enough room to drive a forklift though and turn to pull the gear off shelves and lower it to the floor. The prep process and return process have their unique requirements.
PREP
Prep requires accuracy. Sometimes shorter read lengths allow for the user to operate with greater accuracy with other equipment is nearby the prep area. Meaning if most tags have a read capability, and you are in the middle of an aisle with gear 3' or 4' away your chances of capturing unexpected reads is reduced.
If the tags have larger read lengths such as Global Frequency UHF Metal tags OPP087, consider where you prep items so as not to capture more unexpected reads.
RETURN
RFID functionality combines the ease to track every item and auto-return them from their specific job through the Free Scan In process and improves the speed to batch capture the mass amounts of these assets. Tags with longer read distances might be considered more advantages to capture quicker without the need to be within 1' of the item.
FLEX FUNCTIONALITY
Inventory Setting:
** RFID functionality must be enabled. ** This will be a paid component in the future but is free to access as of now.
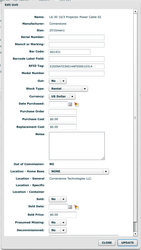
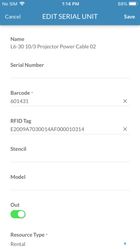
With the addition of RFID functionality, V26 introduces a new field for serialized asset called RFID TAG. This field will be available in both Flex4 and Flex5. We still keep the barcode field so you can have a unique barcode and RFID Tag per asset. See below.
Adding RFID Tags info to an existing serialized asset.
If you are adding a tag to an existing serialized asset there is a fairly simple process.
- Turn Zebra RFD8500 to barcode mode by clicking the Mode button till the green light is on.
- In the Flex5 app goto the QuickLauncher > Inquiry Scan in the dashboard.
- Scan the barcode of the item you want to update the RFID Tag info.
- Select Edit Serial Unit from the Actions
- Click in the RFID Tags Field.
- Change the Zebra RFD8500 to RFID Mode by clicking the Mode button till the green light is off.
- Pull the trigger to read the tag.
- If you are working in an area with many different tags in the vicinity, make sure to point the tag you want to read that is in a different direction the other tags.
- Save updated unit info.
- Close and Repeat.
RFID Batch Capture Mode using Free Scan In
All warehouse screens have a new RFID Icon to the left of the Bluetooth Button to get the user into RFID Batch Capture Mode.
- Click the icon to enter RFID Mode.
- Pull the RFID trigger to read adjacent tags.
- The counter will count up the number of unique tags read.
- Click Preview see valid and invalid tags.
- Any RFID tag received that is connected to a serialized asset in Flex will be counted towards "Valid Units."
- Any RFID tag read that is not assigned to a unit will be counted in the "Invalid Units."
- Invalid tags might be real tags read not assigned to units or
- Invalid tags might be poorly real tags that the reception was interfered with.
- Click the Right Arrow Icon to preview the units for either Valid or Invalid Units.
- Information will include the model image, model description, and barcode associated with the RFID Tag.
- Green Check Marks will appear next to valid units.
- The user can uncheck item they wish not to process.
- Press Scan to scan all checked items.
- Progress Bar counts up to 100%.
- Any items that need attention due to conditions such as Out of Commission, Presumed Missing, Decommissioned or Deleted units will be prompted for the user to address.
- Close to complete the process and return to the screen or New RFID Capture to Capture more assets.
- Flex recommends working in small capture batches to make the review more actionable.